When was the first car made? This intriguing question takes us on a journey through the annals of automotive history, revealing how innovation and engineering evolved over centuries. The automobile has transformed the way we live, work, and travel, marking one of the most significant advancements in human history. In this article, we will explore the origin of the first car, the key figures involved in its creation, and the technological advancements that paved the way for modern vehicles.
The story of the automobile begins long before the invention of the first car. Early concepts of self-propelled vehicles can be traced back to the 15th century, but it wasn't until the 19th century that significant progress was made. This period saw the introduction of steam-powered vehicles, which set the stage for the gasoline-powered cars that we know today. Join us as we dissect the timeline of automotive innovation and uncover the pivotal moments that shaped the industry.
Throughout this article, we will delve into various aspects of automotive history, including the biographical details of key inventors, the evolution of car designs, and the impact of these early vehicles on society. If you're curious about when the first car was made and its journey to modern-day automobiles, keep reading!
Table of Contents
- Biography of Key Inventors
- The First Car: A Historical Overview
- Technological Advancements in Early Automobiles
- Impact of the First Cars on Society
- The Evolution of Car Design
- The Future of Automobiles
- Conclusion
- Sources
Biography of Key Inventors
The invention of the automobile cannot be attributed to a single individual. Instead, it was a collaborative effort that spanned decades and involved numerous inventors. However, a few key figures stand out in this narrative:
| Name | Nationality | Contribution | Year of Birth | Year of Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Karl Benz | German | Invented the first gasoline-powered car | 1844 | 1929 |
| Gottlieb Daimler | German | Pioneered the development of high-speed gasoline engines | 1834 | 1900 |
| Henry Ford | American | Revolutionized mass production of automobiles | 1863 | 1947 |
The First Car: A Historical Overview
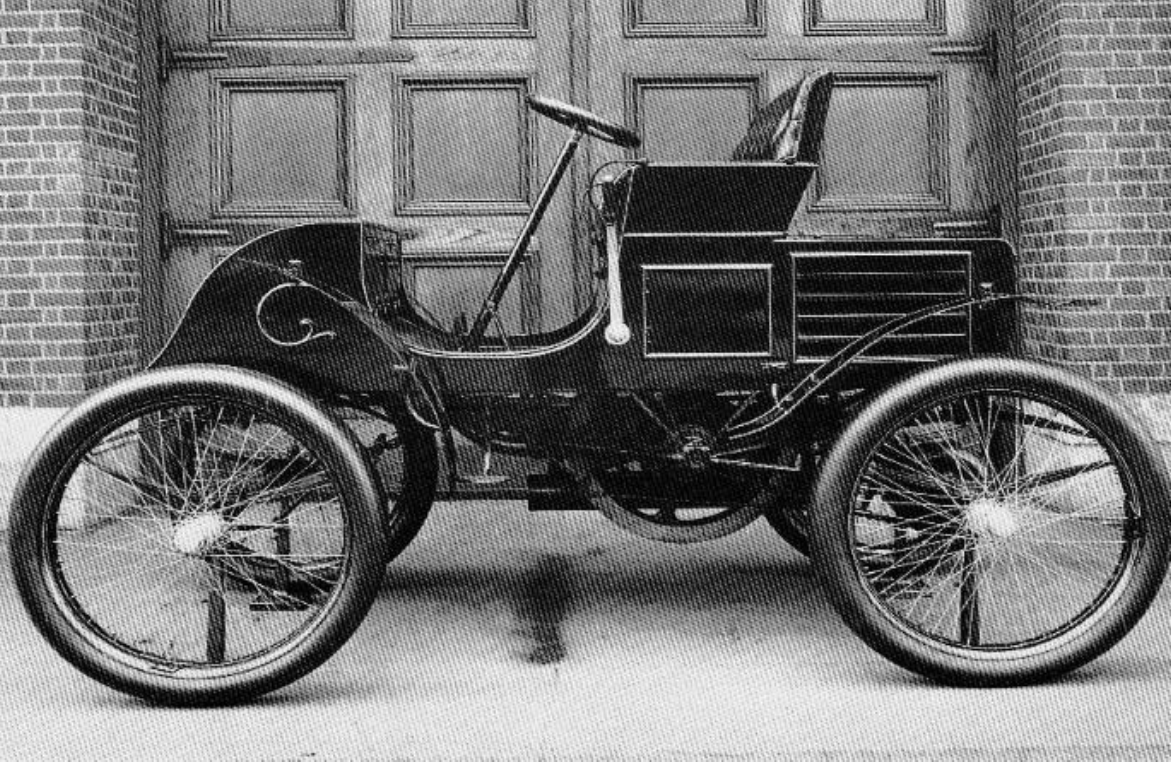
The first true automobile is widely recognized as the Benz Patent-Motorwagen, which was built in 1885 by Karl Benz. This groundbreaking invention was the world's first practical automobile powered by an internal combustion engine. The Motorwagen featured a simple design, with a tubular steel frame and wooden wheels, making it a remarkable engineering achievement for its time.
However, the narrative of the automobile does not end with Benz. Other inventors, such as Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach, were also instrumental in developing early gasoline engines and vehicles. Their innovations contributed to a growing interest in personal transportation, laying the groundwork for the automotive industry.
The Evolution of Early Automobiles
Following the introduction of the Motorwagen, several manufacturers began producing vehicles for commercial sale, including:
- Peugeot (1889) - Produced one of the first gasoline-powered cars.
- Renault (1899) - Introduced a range of innovative designs.
- Ford Motor Company (1903) - Revolutionized the industry with the Model T.
Technological Advancements in Early Automobiles
The development of the automobile was marked by several key technological advancements:
- Internal Combustion Engine: The shift from steam to gasoline engines allowed for more efficient and powerful vehicles.
- Electric Ignition: This innovation improved engine reliability and ease of use.
- Transmission Systems: Advances in gearing and transmission enabled smoother driving experiences.
Introduction of Mass Production
Henry Ford's introduction of the assembly line in the early 20th century revolutionized car production, making automobiles more affordable for the average consumer. The Model T became a symbol of this transformation, selling millions of units and changing the landscape of transportation.
Impact of the First Cars on Society
The advent of the automobile had profound effects on society:
- Improved Mobility: Cars enabled people to travel longer distances, reshaping communities.
- Economic Growth: The automotive industry created millions of jobs and stimulated related sectors.
- Cultural Changes: Cars became symbols of freedom and status, influencing popular culture.
The Evolution of Car Design
From the early days of the Motorwagen to modern automobiles, car design has undergone significant changes. Key design evolutions include:
- Streamlined Shapes: Aerodynamic designs became more common in the mid-20th century.
- Safety Features: Incorporation of seat belts, airbags, and anti-lock brakes improved passenger safety.
- Technological Integration: Modern cars now feature advanced technology, such as GPS, infotainment systems, and electric drivetrains.
The Future of Automobiles
As we look ahead, the future of automobiles appears promising and challenging. Key trends shaping the future include:
- Electric Vehicles: A growing emphasis on sustainability is driving the shift towards electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Autonomous Driving: Advances in AI and machine learning are paving the way for self-driving cars.
- Smart Technology: Integration of smart features will continue to enhance driver and passenger experiences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of the automobile began with the invention of the first car, the Benz Patent-Motorwagen, in 1885. Through the contributions of various inventors and key technological advancements, the automotive industry has evolved dramatically over the years. The impact of these innovations has reshaped society, providing improved mobility, economic growth, and cultural changes. As we look to the future, the industry will continue to adapt to new challenges and opportunities, paving the way for a new era of transportation.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and insights in the comments section below. If you found this article informative, consider sharing it with others or exploring more articles on our site!
Sources
For further reading and verification of the information provided, please refer to the following sources: